JUN
23
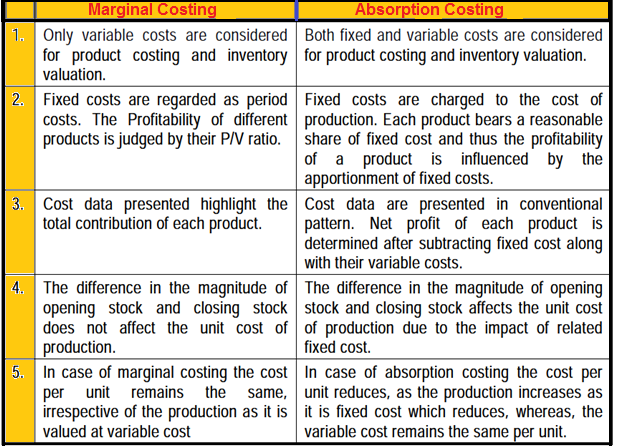
Variable and fixed costs play into the degree of operating leverage a company has. In short, fixed costs are more risky, generate a greater degree of leverage, and leave the company with greater upside potential. On the other hand, variable costs are safer, generate less leverage, and leave the company with a smaller upside potential. Understanding life in pieces on cbs how variable costs impact margins and net income allows manufacturing companies to optimize profitability. If you want to optimize operations and boost profitability, understanding cost management is a must. One of the more important aspects of cost management is variable cost, as it directly impacts a manufacturing company’s bottom line.
Variable Costing vs. Absorption Costing
We’re a headhunter agency that connects US businesses with elite LATAM professionals who integrate seamlessly as remote team members — aligned to US time zones, cutting overhead by 70%. The definitions of full costing and costing variables and their strengths and weaknesses are provided below, along with examples. Production is estimated to hold steady at \(5,000\) units per year, while sales estimates are projected to be \(5,000\) units in year \(1\); \(4,000\) units in year \(2\); and \(6,000\) in year \(3\).
What are the primary components that make up variable costs?
Half of the $40,000 in fixed production cost ($20,000) will be included in inventory at the end of the period, thereby lowering expenses on the income statement and increasing profit by $20,000. At some point, this will catch up to the manager because the company will have excess or obsolete inventory in future months. However, in the short run, the manager will increase profit by increasing production. This strategy does not work with variable costing because all fixed manufacturing overhead costs are expensed as incurred, regardless of the level of sales. Under absorption costing, fixed manufacturing overhead costs allocated to units produced are included in inventory values on the balance sheet. In contrast, variable costing excludes fixed overhead costs from inventory.
What Is the Formula for Total Variable Cost?
- Ethical business managers understand the benefits of using the appropriate costing systems and methods.
- Instead of focusing on the overhead costs incurred by the product unit, these methods focus on assigning the fixed overhead costs to inventory.
- As you can see, variable costing gives managers key insights into profit drivers.
- Variable costing provides a more accurate picture of your cash flow, which is critical for small manufacturers operating with tighter margins.
- Since variable costing treats fixed manufacturing overhead costs as period costs, all fixed manufacturing overhead costs are expensed on the income statement when incurred.
For most of you who may still be confused about choosing the suitable method for your business, the continuation of this article can add to your insight before making the appropriate choice.
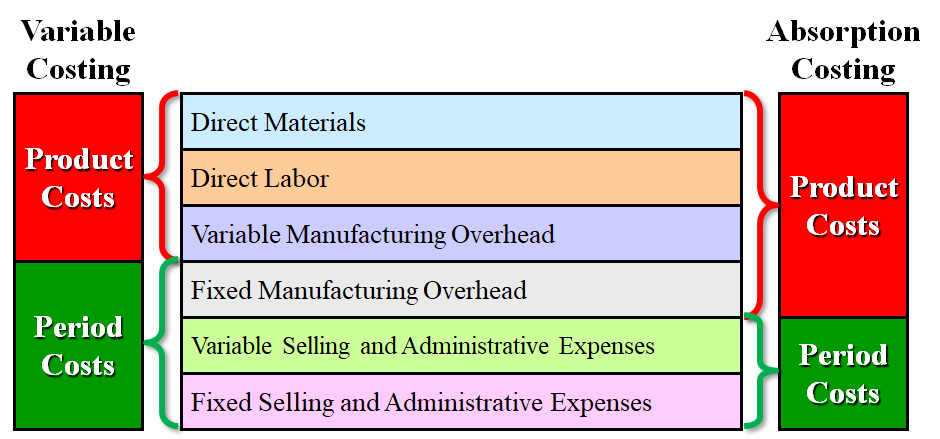
Thus when more units are produced than are sold, variable costing results in higher costs and lower profit. If absorption costing is the method acceptable for financial reporting under GAAP, why would management prefer variable costing? Advocates of variable costing argue that the definition of fixed costs holds, and fixed manufacturing overhead costs will be incurred regardless of whether anything is actually produced. Outdoor Nation, a manufacturer of residential, tabletop propane heaters, wants to determine whether absorption costing or variable costing is better for internal decision-making.
Is Variable Costing More Useful Than Absorption Costing?
The impact of variable costs on the breakeven point depends on the cost structure of the business, alongside its pricing strategy and sales volume. Reduction in variable costs can result in a lower breakeven point, increasing the possibility of generating profit at lower sales volumes. Some common examples of variable costs include direct materials, direct labor, and transaction fees. These costs vary depending on the quantity of goods or services produced by a company. By calculating and analyzing variable costs, businesses can make better-informed decisions on pricing, production levels, and overall cost management strategies. Variable costing is a concept used in managerial and cost accounting in which the fixed manufacturing overhead is excluded from the product-cost of production.
The variable cost per unit is \(\$22\) (the total of direct material, direct labor, and variable overhead). The absorption cost per unit is the variable cost (\(\$22\)) plus the per-unit cost of \(\$7\) (\(\$49,000/7,000\) units) for the fixed overhead, for a total of \(\$29\). Examples of variable costs are sales commissions, direct labor costs, cost of raw materials used in production, and utility costs. The break-even point determines the level of sales needed to cover all of the costs of production; fixed and variable costs. If a company is at the break-even point, they are neither making nor losing money.
Variable cost and average variable cost may not always be equal due to price increases or pricing discounts. An employee’s hourly wages are a variable cost; however, that employee was promoted last year. The current variable cost will be higher than before; the average variable cost will remain something in between. The cost to package or ship a product will only occur if a certain activity is performed.
This means that businesses that use variable costing may need to maintain two sets of accounting records – one for internal management purposes and one for external financial reporting. On the other hand, a low operating leverage means that the company’s expenses are primarily variable costs, implying less sensitivity to changes in sales. While increased sales may not dramatically improve profit margins in this scenario, the company is better positioned to withstand declines in sales without facing severe losses. In conclusion, effectively managing variable costs through monitoring production levels and optimizing labor and materials usage can significantly improve a business’s profitability. Implementing these strategies can help businesses maintain an acceptable profit margin while staying competitive in the market. Different industries may have varying levels of variable costs, and companies must account for these costs in their financial statements and budgeting processes.
They have both a fixed component that remains constant no matter the production level and a variable component that changes with the production or sales volume. For example, the cost of a mobile data plan might have a fixed base charge and a variable cost per gigabyte of data used. These help managers understand production targets, set sales goals, and mitigate risks. Overall, variable costing is a valuable tool for pricing decisions, profitability analysis, evaluating risk, and cost management. In managerial accounting and financial modeling, variable costs play an important role in break-even analysis, contribution margin calculations, budgeting, cost-volume-profit analysis, and more. Tracking which costs are fixed vs. variable is crucial for making sound business decisions.
Raw materials are the direct goods purchased that are eventually turned into a final product. If the athletic brand doesn’t make the shoes, it won’t incur the cost of leather, synthetic mesh, canvas, or other raw materials. In general, a company should spend roughly the same amount on raw materials for every unit produced assuming no major differences in manufacturing one unit versus another.





